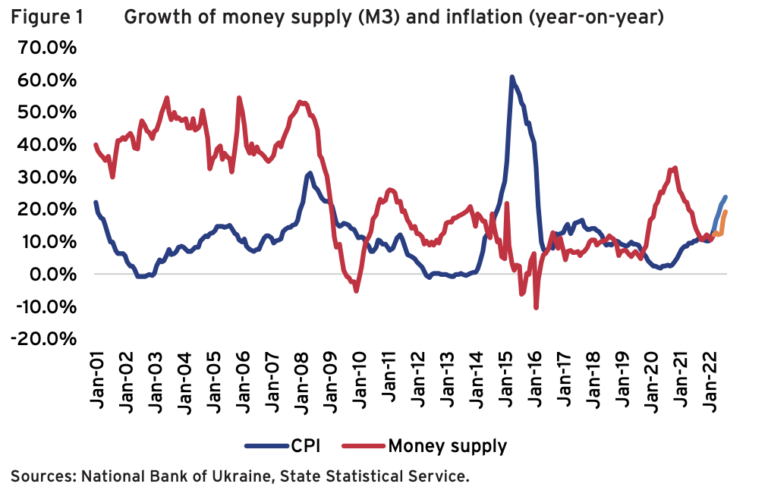
Financing Ukraine’s victory
Ukraine has just achieved a stunning success on the battlefield in the Kharkiv counteroffensive, showing that it can win the war. However, we see a

Ukraine has just achieved a stunning success on the battlefield in the Kharkiv counteroffensive, showing that it can win the war. However, we see a
As the conflict in Ukraine continues on into the latter months of 2022, this book outlines macroeconomic policies to put the economy of Ukraine on

In this article we list popular yet erroneous approaches to economic policies, explain what is wrong with them and elaborate on which policies would really

Justifying their stay in Russia by “provision of essential goods” is a poor excuse. In reality, companies that claim this are protecting their market share.

Ukraine’s economy continues to operate despite the battering the country is getting from the Russian military. Many factories and businesses still function. Other industries like

We use a unique high-frequency Russian customs data to evaluate the impact of international sanctions on Russia. We focus on Russian crude oil and oil products exports, as they are the key sources of export revenues and government finances. We find that Russia was able to redirect crude oil exports from Europe to alternative markets such as India, China, and Turkey with no loss of volumes. In particular, we find that Russian oil exports from Pacific Ocean ports, which are critical for trade with China, do not comply with the G7 price cap.
By Tania Babina, Benjamin Hilgenstock, Oleg Itskhoki, Maxim Mironov, and Elina Ribakova

The EU has banned most of Russia’s oil exports, but little action has been taken on natural gas trade. This column argues for a disclosure requirement targeted at gas traders, detailing the share of gas they buy from Russian sources. Such a measure would address the information deficit for consumers and empower supportive citizens and businesses to switch away from Russian gas. As an additional benefit, this measure would accelerate the clean energy transition in Europe.
By Iryna Sikora and Boris Vallee

Russia is one of the top three fossil fuel producers in the world, and its economy relies heavily on revenues from oil and natural gas. A full embargo on Russian energy today by the EU alone would already decrease its GDP per capita by 1,500-2,500 USD (or 10 to 25%), a significant reduction to weaken Moscow’s capacity to sustain its aggression against Ukraine.
By Kevin Berry and Iryna Sikora
Donations are collected through the AI for Good Foundation, an IRS 501(c)3 Public Charity (81-1631000)